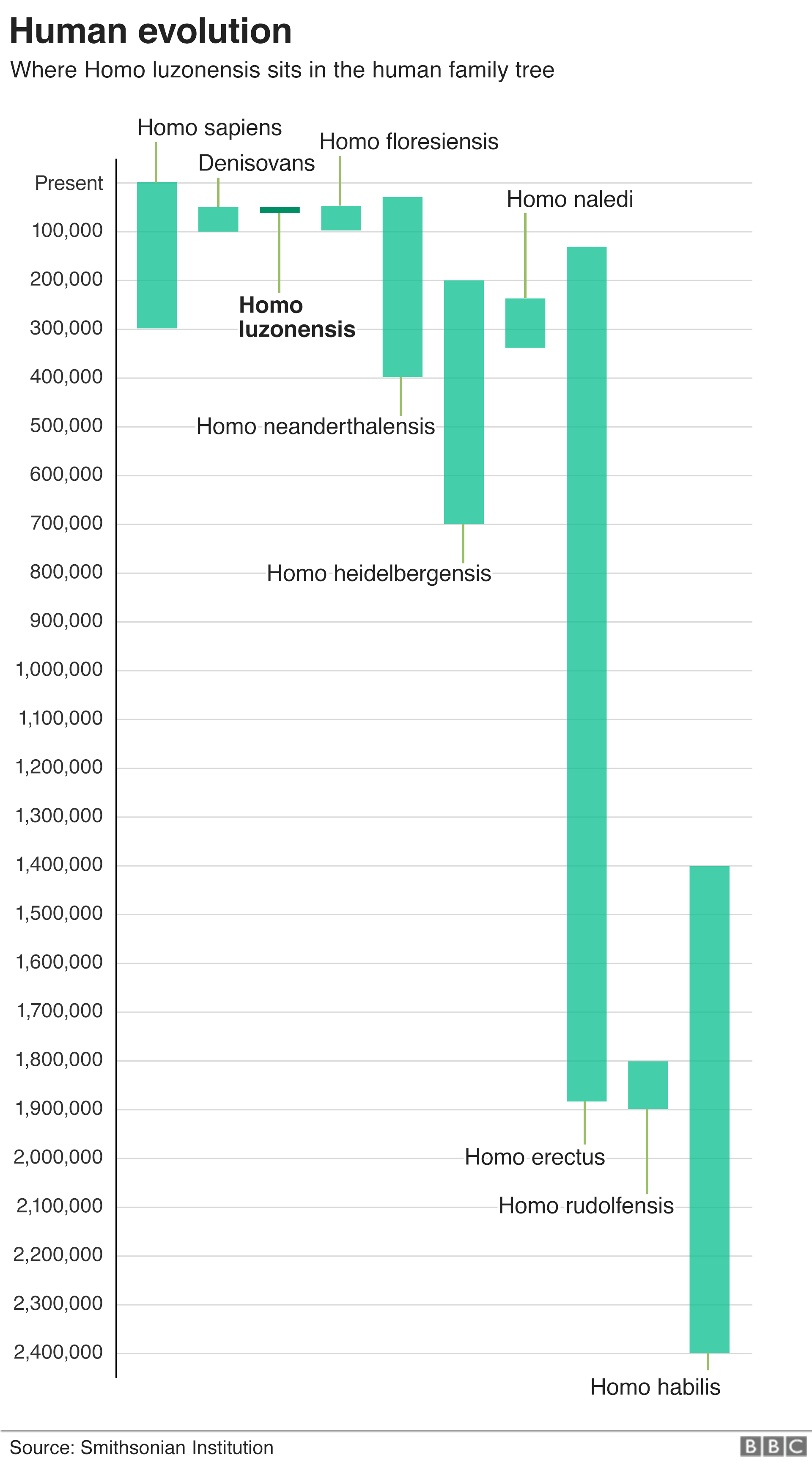
Homo luzonensis teeth look like those of more recent members of our genus Homo but the hand and foot bones look more like they could. The small-bodied hominin named Homo luzonensis lived on the island of Luzon at least 50000 to 67000 years ago.
Homo Luzonensis A New Species Is Added To The Human Family Tree
Sapiens and Asian H.

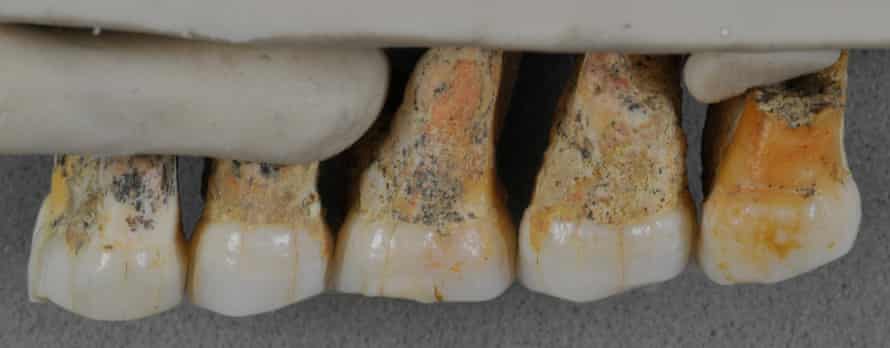
Homo luzonensis 3 features of modern man. Sapiens 2101 Early Homo. However Falks scans of LB1s pituitary fossa show that it is not larger than usual. Two premolar and three molar teeth proved especially useful because they stemmed from the same individual.
The newfound species is named Homo luzonensis in honor of Luzon the island where the mysterious beings lived during the late Pleistocene epoch more than 50000 years agoAt less than 4 feet 12. The timeline of human evolution outlines the major events in the evolutionary lineage of the modern human species Homo sapiens throughout the history of life beginning some 42 billion years ago down to recent evolution within H. Homo erectus species lived between 100000 and 16 million years ago although some estimates extend this to between 35000 and 18 million years ago.
Erectus teeth but they were too small to have stemmed from H. Rhodesiensis and the Gawis cranium 27 Neanderthal and Denisovan 28 H. The two species share a mix of modern and older traits.
They said that various features of H. Luzonensis teeth for example have a hodge podge of traits that match the teeth of Homo sapiens Homo erectus and another smaller-brained human ancestor Paranthropus in different ways. The curve in their hands and feet are similar to toes and finger bones that belonged to the three-million-year-old Australopithecus afarensis but their molars are similar to that of the modern human.
Homo from Latin homō man is the genus that emerged in the otherwise extinct genus Australopithecus that encompasses the extant species Homo sapiens modern humans plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related to modern humans depending on the species most notably Homo erectus and Homo neanderthalensisThe genus emerged with the appearance of Homo. Sapiens during and since the Last Glacial Period. It includes brief explanations of the various taxonomic ranks in the human lineage.
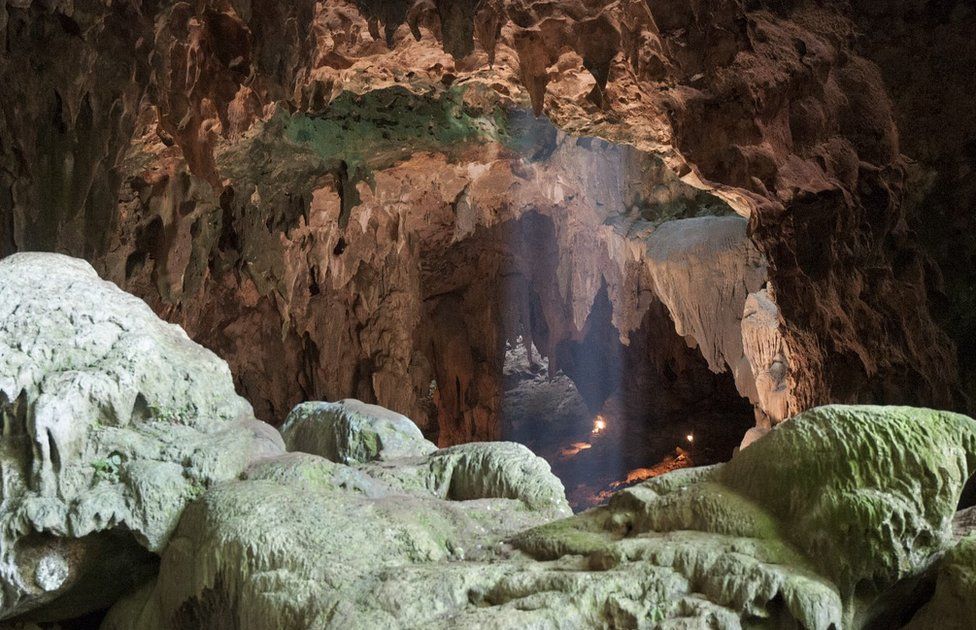
Homo luzonensis shares different traits with many of its relatives including Neanderthals modern humans and Hobbit humans Callao Cave Archaeology Project Its quite incredible the hand and. Mijares explained that before he found Homo luzonensis there were only three species from the human family tree that was proven to have existed in Southeast Asia the modern man Homo sapiens the 2-million-year-old Homo erectus and the dwarf Homo floresiensis dubbed The Hobbit. Fossilized teeth and bones from at least three individuals found in Callao Cave on Luzons northern coast were dated to just 50000 and 67000 years ago.
Bone structures suggest that the Homo luzonensis grew no more than four feet. The homininidentified from a total of seven teeth and six small boneshosts. They were initially identified as belonging to modern humans in 2010 but in 2019.
Moreover they didnt go extinct long ago. This suggests Homo luzonensis might like Australopithecus have had the ability to easily climb trees as well as walk upright on two legs though its not clear whether they did so. Floresiensis are diagnostic characteristics such as enlarged pituitary fossa unusually straight and untwisted humeral heads relatively thick limbs double rooted premolar and primitive wrist morphology.
Homo luzonensis also locally called ubag after a mythical caveman is an extinct possibly pygmy species of archaic human from the Late Pleistocene of Luzon the PhilippinesTheir remains teeth and phalanges are only known from Callao Cave in the northern part of the island dating to before 50000 years ago. The molars had modern features reminiscent of H. They were definitely contemporary with Homo sapiens in the region if not necessarily on Luzon.
List of human evolution fossils 1 Table of species 2 Evolution of genus Homo 21 H. Homo luzonensis has some physical similarities to recent humans but in other features hark back to the australopithecines upright-walking ape-like creatures that lived in Africa between two and. In 2004 another group announced the discovery 3 of Homo floresiensis also known as the Hobbit a species that would have stood just over a metre in height on the Indonesian island of Flores.
Some of Homo luzonensis features were primitive like Australopithecus and some were modern like the more advanced Homo genus the researchers report. After years of searching Indonesia for the missing link Dutchman Eugene Dubois finally uncovered part of a skull in 1891 known as Java Man.
 Homo Luzonensis New Human Species Found In Philippines Bbc News
Homo Luzonensis New Human Species Found In Philippines Bbc News
 New 4ft Human Species With Curved Fingers And Toes Discovered In Philippines Cave
New 4ft Human Species With Curved Fingers And Toes Discovered In Philippines Cave
 New Species Of 4ft Ancient Human Discovered In Philippines Cave The Independent The Independent
New Species Of 4ft Ancient Human Discovered In Philippines Cave The Independent The Independent
Homo Luzonensis A New Species Is Added To The Human Family Tree
 New Species Of Ancient Human Discovered In The Philippines Homo Luzonensis
New Species Of Ancient Human Discovered In The Philippines Homo Luzonensis
 New Species Of Ancient Human Discovered In Philippines Cave Evolution The Guardian
New Species Of Ancient Human Discovered In Philippines Cave Evolution The Guardian
 New Species Of Ancient Human Discovered In Philippines Cave Evolution The Guardian
New Species Of Ancient Human Discovered In Philippines Cave Evolution The Guardian
 Fossil Finds Elwyn S Evolution Page
Fossil Finds Elwyn S Evolution Page
 A New Species Of Human Homo Luzonensis Discovered In The Philippines University Of Bordeaux
A New Species Of Human Homo Luzonensis Discovered In The Philippines University Of Bordeaux
 Homo Luzonensis New Human Species Found In Philippines Bbc News
Homo Luzonensis New Human Species Found In Philippines Bbc News
 Homo Luzonensis Facts About The Latest Hominid Discovered What S On
Homo Luzonensis Facts About The Latest Hominid Discovered What S On
 Number Of Ancient Humans Continues To Grow After Discovery Chemainus Valley Courier
Number Of Ancient Humans Continues To Grow After Discovery Chemainus Valley Courier
 New Species Of Ancient Human Discovered In The Philippines Homo Luzonensis
New Species Of Ancient Human Discovered In The Philippines Homo Luzonensis
Homo Luzonensis A New Species Is Added To The Human Family Tree
 New Species Of 4ft Ancient Human Discovered In Philippines Cave The Independent The Independent
New Species Of 4ft Ancient Human Discovered In Philippines Cave The Independent The Independent
 Dr Chris Stringer The Lovepost
Dr Chris Stringer The Lovepost

